
 


|
|
|
|
Architecture
|
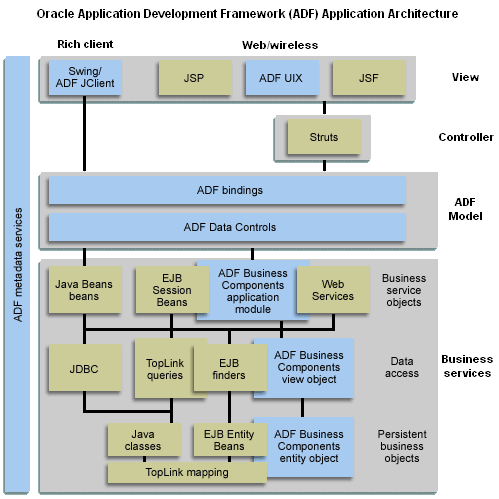
Based on the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture, Oracle
ADF lets you focus your energies on the business problem, rather
than on the underlying technologies needed to implement the solution.
Oracle ADF offers pluggable technologies for the model, view,
and controller, allowing you to make implementation choices at
the various layers of the architecture.
|
|
|
|
All layers of the Oracle ADF framework offer declarative options
for development, configured from XML metadata, while accommodating
custom coding wherever necessary. You can choose to use all or
part of the framework in the applications you build.
When you work with ADF, you and your application development
team can quickly create an entire J2EE application with these
supported components:
- Model layer: A thin model layer that adapts and combines a
full range of business services as desired, including Oracle
ADF Business Components, TopLink mappings, JavaBeans, Enterprise
JavaBeans, and web services.
- Controller layer: For web applications, you can design page
flows to run in the Jakarta Struts servlet controller. For Java
client applications, controller functionality is provided by
the UI components in the Swing toolkit and is therefore not
addressed as a separate layer.
- View layer: For web applications, you can design JSP pages,
or you can work with Oracle ADF UIX, which provides its own
set of XML-based UI components. For Java client applications,
you will work with the standard Swing UI components to design
Java forms and the Swing extension, Oracle ADF JClient.
|
|

