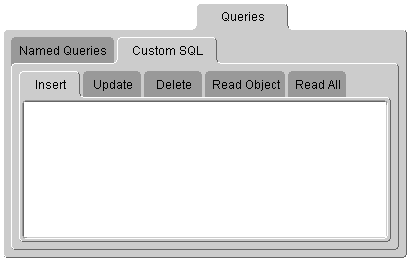
Figure 4-2 Queries Custom SQL Tab
Note: The TopLink Mapping editor does not validate the SQL code that you enter. The code is defined by the specific database type.
Use the Queries tab to specify TopLink Expressions, EJB QL queries, and SQL queries to access the database. EJB QL is a declarative language that presents queries from an object-model perspective. Refer to the EJB specification for detailed information.
For 2.0 CMP projects, the ejb-jar.xml file stores query lists. You can define the queries in the file and then read them into the TopLink Mapping editor, or define them on the Queries tab and write them to the file.
To create queries:
Use this procedure to create custom SQL queries for the TopLink descriptor.
To create custom SQL queries:
Figure 4-2 Queries Custom SQL Tab

Example 4-1 Custom Queries
To control the five custom query tabs, you can include your own query object or SQL string for a particular descriptor. The SQL string for each database is defined by the type of database.
For example, the stored procedure to read an object may use the following string:
Read_Employee(EMP_ID=>4653) The query manager requires the following string to read the object:
Read_Employee(EMP_ID=>#EMP_ID) Use named queries to specify SQL, EJB QL, or TopLink Expression queries to access the database.
To create a named query:
Figure 4-3 Queries Tab
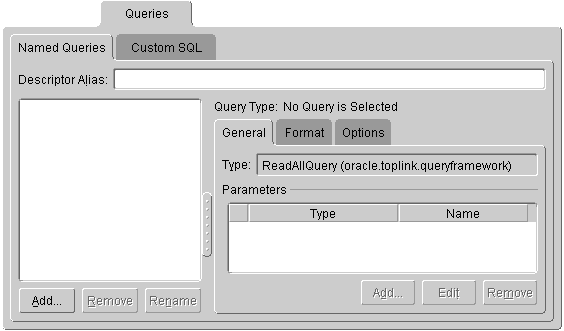
Figure 4-4 Queries General Tab
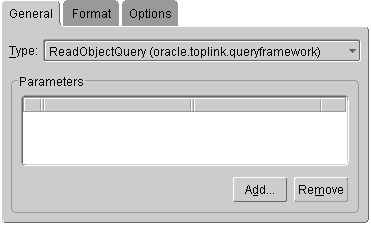
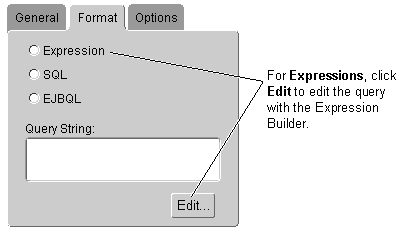
Figure 4-5 Queries Format Tab
findOneByQuery and findManyByQuery.Figure 4-6 Queries Options Tab
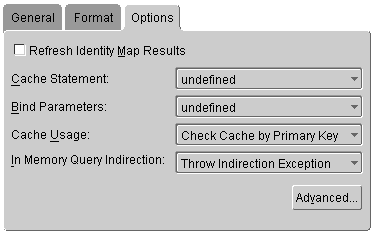
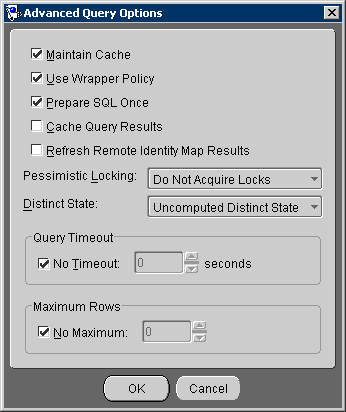
Figure 4-7 Advanced Query Options
Copyright © 1997, 2004, Oracle. All rights reserved.