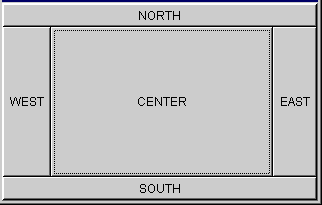
BorderLayout arranges a container's components in areas
named North, South, East, West, and Center.
The components in North and South are given their preferred height and are stretched across the full width of the container.
The components in East and West are given their preferred width and are stretched vertically to fill the space between the north and south areas.
A component in the Center expands to fill all remaining space.

BorderLayout is good for forcing components to one or more
edges of a container, and for filling up the center of the container
with a component. It is also the layout you want to use to cause a
single component to completely fill its container.
You will probably find BorderLayout to be the most useful
layout manager for the larger containers in your UI. By nesting a panel
inside each area of the BorderLayout, then populating each
of those panels with other panels of various layouts, you can achieve
quite complicated UI designs.
Components are positioned in one of five areas within a
BorderLayout, based on the constraints property. You
can set the constraints property for the component in the
Inspector to one of the following values: North, South, East, West, or
Center.
For example, to put a toolbar across the top of a BorderLayout
container, you could create a FlowLayout panel of buttons and
place it in the North area of the container. You do this by selecting
the panel and choosing North for its constraints property
in the Inspector.
To set the constraints property:
constraints property in the Inspector, and
click its value field.
constraints property dropdown
list and select the area you want the component to occupy.
If you use JDeveloper's Java Visual Editor to change the layout of an
existing container to BorderLayout, the components near the
edges automatically move to fill the closest edge. A component near the
center may be set to Center. If a component moves to an unintended
location, you can correct the constraints property in the
Inspector, or drag the component to a new position in the Java Visual
Editor.
Each of the five areas can contain any number of components (or panel of components), however, unless the topmost component is not opaque, any lower components in the same area will be covered by the topmost one.
The following are some general guidelines for working with multiple
components and BorderLayout:
XYLayout first to move the components to their
approximate intended positions, with only one component near each edge.
Note:BorderLayout ignores the order in
which you add components to the container.
By default, a BorderLayout puts no gap between the
components it manages. However, you can use the Inspector to specify the
horizontal or vertical gap in pixels for a BorderLayout
associated with a container.
To modify the gap surrounding BorderLayout components,
select the BorderLayout object in the Structure window
(displayed immediately below the container it controls), then modify the
pixel value in the Property Inspector for the hgap and
vgap properties.
Working with Nested Panels and Layouts.
Copyright © 1997, 2004, Oracle. All rights reserved.